FILE PHOTO – Robotic arms spot welds on the chassis of a Ford Transit Van under assembly at the Ford Claycomo Assembly Plant in Claycomo, Missouri April 30, 2014. (Photo: REUTERS)
There’s a meme on Facebook and Twitter that asks people to “confess your unpopular opinions.” I suppose I could play that game by saying that I’d rather eat fast food than patronize most fancy restaurants (especially if I have to pay the bill!). And I’ve unintentionally played that game already by admitting that politicians aren’t always sinister and evil.
But I have something even more astounding to confess: My leftist friends are right when they assert that the free market destroys jobs.
Not only are they right, they probably underestimate the number of jobs that are destroyed by capitalism. Over time, millions of jobs vanish because of the greedy pursuit of profits.
Mark Perry of the American Enterprise Institute shares some very sobering data on how almost all of the big companies of the 1950s have faded over the past 60 years.
Comparing the Fortune 500 companies in 1955 to the Fortune 500 in 2014, there are only 61 companies that appear in both lists. In other words, only 12.2% of the Fortune 500 companies in 1955 were still on the list 59 years later in 2014, and almost 88% of the companies from 1955 have either gone bankrupt, merged, or still exist but have fallen from the top Fortune 500 companies (ranked by total revenues). Most of the companies on the list in 1955 are unrecognizable, forgotten companies today (e.g. Armstrong Rubber, Cone Mills, Hines Lumber, Pacific Vegetable Oil, and Riegel Textile). …That’s a lot of churning and creative destruction, and it’s probably safe to say that almost all of today’s Fortune 500 companies will be replaced by new companies in new industries over the next 59 years.
And why did these companies disappear or shrink in size, thus leading to major job losses?
Mostly because capitalists, seeking profits, invested money in ways that displaced old technologies, hurt old competitors, and made old products less attractive.
Sounds terrible, right? Jobs are lost because of greedy rich people trying to increase their wealth.
And if you’re one of the people in the unemployment line, it is terrible.
But keep in mind that this process of creative destruction led to new technologies, new competitors and new products. And the net effect of all these changes is that – on average – we are much richer.
Mark elaborates.
…for that we should be thankful. The constant turnover in the Fortune 500 is a positive sign of the dynamism and innovation that characterizes a vibrant consumer-oriented market economy… In the end, the creative destruction that results in a constantly changing group of Fortune 500 companies is driven by the endless pursuit of sales and profits that can only come from serving customers with low prices, high quality and great service.
Indeed, this system is what has given us the “hockey stick” of human progress.
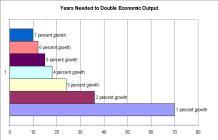 All this disruption and change is what enables our society, over time, to grow faster and produce more goods and services and lower prices.
All this disruption and change is what enables our society, over time, to grow faster and produce more goods and services and lower prices.
At least when the market is allowed to operate with the right set of policies – what I call the recipe for growth and prosperity.
In my speeches, I sometimes make similar points by using historical examples.
- I ask audiences to think about how personal computers have made our lives more enjoyable and productive, but I then ask them to ponder what happened to the people who had jobs making, selling, and servicing typewriters.
- I ask audiences to think about how the automobile boosted productivity and increased mobility, but I then ask them to consider the lost jobs of people in the horse and buggy industry.
- I ask audiences to think about how electrification and the light bulb improved the economy in countless ways, but I then ask them to speculate on the number of jobs that were destroyed in the candle-making sector.
The sad reality is that progress has a price tag. Yes, we are far richer because of great inventions that boosted productivity and improved lives. But that doesn’t change the fact that real workers with real families often experienced genuine anguish when jobs in some sectors disappeared. And that’s still happening today.
And workers are largely blameless when job losses occur. All they did was exchange honest work for honest pay. It was the capitalists who made mistakes by not managing companies effectively and not allocating capital efficiently (or, to be more charitable, they simply failed to anticipate major changes that were about to occur).
By the way, this isn’t an argument for government intervention. We would be much poorer today if politicians tried to save jobs every time there was creative destruction in the economy. Perhaps most important, every job that they “saved” would be offset by the jobs (and prosperity) that weren’t created or didn’t materialize because the clumsy foot of government replaced the invisible hand of the market.
What Bastiat taught the world in the 1800s is still true today. We have to consider both the seen (the jobs that are saved) and the unseen (the greater number of jobs that don’t get created) when contemplating the impact of government.
This is why I want the economy to be as dynamic and innovative as possible so that displaced workers can find new positions as quickly as possible, hopefully earning even more money.
Here’s a short video from Learn Liberty that teaches about this process of creative destruction.
[brid video=”86067″ player=”2077″ title=”How to Sabotage Progress Learn Liberty”]