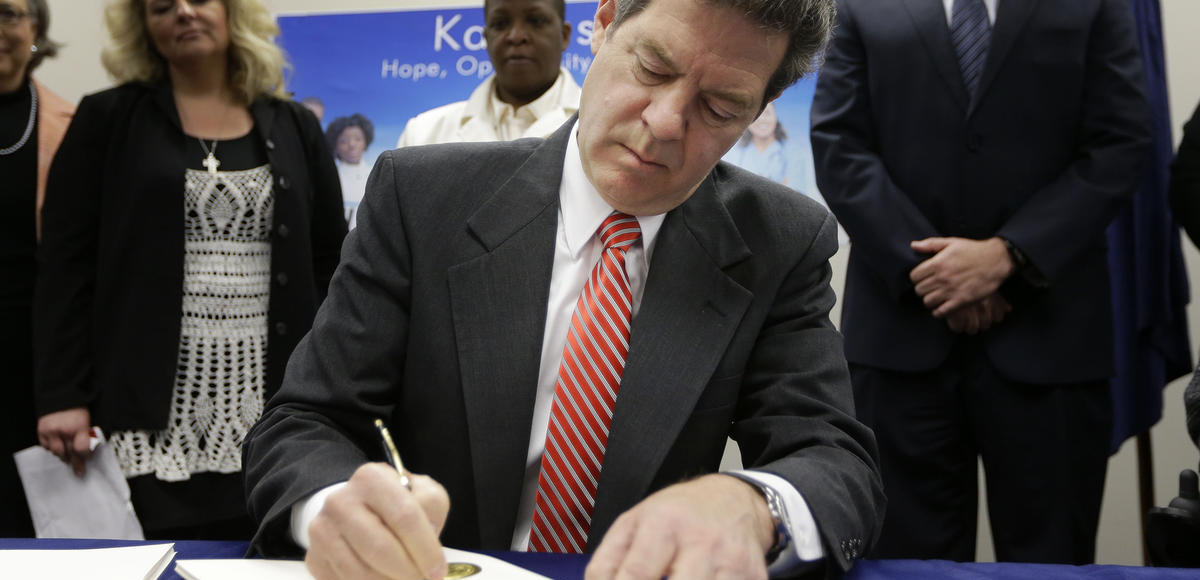

Gov. Sam Brownback signs a welfare reform bill into law in Topeka, Kan., Thursday, April 16, 2015.
(Photo: AP)
Leftist don’t have many reasons to be cheerful. Global economic developments keep demonstrating (over and over again) that big government and high taxes are not a recipe for prosperity. That can’t be very encouraging for them.
They also can’t be very happy about the Obama presidency. Yes, he was one of them, and he was able to impose a lot of his agenda in his first two years. But that experiment with bigger government produced very dismal results. And it also was a political disaster for the left since Republicans won landslide elections in 2010 and 2014 (you could also argue that Trump’s election in 2016 was a repudiation of Obama and the left, though I think it was more a rejection of the status quo).
But there is one piece of good news for my statist friends. The tax cuts in Kansas have been partially repealed. The New York Times is overjoyed by this development.
The Republican Legislature and much of Kansas has finally turned on Gov. Sam Brownback in his disastrous five-year experiment to prove the Republicans’ “trickle down” fantasy can work in real life — that huge tax cuts magically result in economic growth and more, not less, revenue. …state lawmakers who once abetted the Brownback budgeting folly passed a two-year, $1.2 billion tax increase this week to begin repairing the damage. …It will take years for Kansas to recover.
And you won’t be surprised to learn that Paul Krugman also is pleased.
Here’s some of what he wrote in his NYT column.
…there was an idea, a theory, behind the Kansas tax cuts: the claim that cutting taxes on the wealthy would produce explosive economic growth. It was a foolish theory, belied by decades of experience: remember the economic collapse that was supposed to follow the Clinton tax hikes, or the boom that was supposed to follow the Bush tax cuts? …eventually the theory’s failure was too much even for Republican legislators.
Another New York Times columnist did a victory dance as well.
The most momentous political news of the past week…was the Kansas Legislature’s decision to defy the governor and raise income taxes… Kansas, under Gov. Sam Brownback, has come as close as we’ve ever gotten in the United States to conducting a perfect experiment in supply-side economics. The conservative governor, working with a conservative State Legislature, in the home state of the conservative Koch brothers, took office in 2011 vowing sharp cuts in taxes and state spending, except for education — and promising that those policies would unleash boundless growth. The taxes were cut, and by a lot.
Brownback’s supply-side experiment was a flop, the author argues.
The cuts came. But the growth never did. As the rest of the country was growing at rates of just above 2 percent, Kansas grew at considerably slower rates, finally hitting just 0.2 percent in 2016. Revenues crashed. Spending was slashed, even on education… The experiment has been a disaster. …the Republican Kansas Legislature faced reality. Earlier this year it passed tax increases, which the governor vetoed. Last Tuesday, the legislators overrode the veto. Not only is it a tax increase — it’s even a progressive tax increase! …More than half of the Republicans in both houses voted for the increases.
If you read the articles, columns, and editorials in the New York Times, you’ll notice there isn’t a lot of detail on what actually happened in the Sunflower State. Lots of rhetoric, but short on details.
So let’s go to the Tax Foundation, which has a thorough review including this very helpful chart showing tax rates before the cuts, during the cuts, and what will now happen in future years (the article also notes that the new legislation repeals the exemption for small-business income).
We know that folks on the left are happy about tax cuts being reversed in Kansas. So what are conservatives and libertarians saying?
The Wall Street Journal opined on what really happened in the state.
…national progressives are giddy. Their spin is that because the vote reverses Mr. Brownback’s tax cuts in a Republican state that Donald Trump carried by more than 20 points, Republicans everywhere should stop cutting taxes. The reality is more prosaic—and politically cynical. …At bottom the Kansas tax vote was as much about unions getting even with the Governor over his education reforms, which included making it easier to fire bad teachers.
And the editorial also explains why there wasn’t much of an economic bounce when Brownback’s tax cuts were implemented, but suggests there was a bit of good news.
Mr. Brownback was unlucky in his timing, given the hits to the agricultural and energy industries that count for much of the state economy. But unemployment is still low at 3.7%, and the state has had considerable small-business formation every year since the tax cuts were enacted. The tax competition across the Kansas-Missouri border around Kansas City is one reason Missouri cut its top individual tax rate in 2014.
I concur. When I examined the data a few years ago, I also found some positive signs.
In any event, the WSJ is not overly optimistic about what this means for the state.
The upshot is that supposedly conservative Kansas will now have a higher top marginal individual income-tax rate (5.7%) than Massachusetts (5.1%). And the unions will be back for another increase as spending rises to meet the new greater revenues. This is the eternal lesson of tax increases, as Illinois and Connecticut prove.
And Reason published an article by Ben Haller with similar conclusions.
What went wrong? First, the legislature failed to eliminate politically popular exemptions and deductions, making the initial revenue drop more severe than the governor planned. The legislature and the governor could have reduced government spending to offset the decrease in revenue, but they also failed on that front. Government spending per capita remained relatively stable in the years following the recession to the present, despite the constant fiscal crises. In fact, state expenditure reports from the National Association of State Budget Officers show that total state expenditures in Kansas increased every year except 2013, where expenditures decreased a modest 3 percent from 2012. It should then not come as a surprise that the state faced large budget gaps year after year. …tax cuts do not necessarily pay for themselves. Fiscal conservatives, libertarians, …may have the right idea when it comes to lowering rates to spur economic growth, but lower taxes by themselves are not a cure-all for a state’s woes. Excessive regulation, budget insolvency, corruption, older demographics, and a whole host of other issues can slow down economic growth even in the presence of a low-tax environment.
Since Haller mentioned spending, here’s another Tax Foundation chart showing inflation-adjusted state spending in Kansas. Keep in mind that Brownback was elected in 2010. The left argued that he “slashed” spending, but that assertion obviously is empty demagoguery.
Now time for my two cents.
Looking at what happened, there are three lessons from Kansas.
By the way, all three points are why the GOP is having trouble in Washington.
The moral of the story? As I noted when writing about Belgium, it’s hard to have good tax policy if you don’t have good spending policy.
The most damning journalistic sin committed by the media during the era of Russia collusion…
The first ecological study finds mask mandates were not effective at slowing the spread of…
On "What Are the Odds?" Monday, Robert Barnes and Rich Baris note how big tech…
On "What Are the Odds?" Monday, Robert Barnes and Rich Baris discuss why America First…
Personal income fell $1,516.6 billion (7.1%) in February, roughly the consensus forecast, while consumer spending…
Research finds those previously infected by or vaccinated against SARS-CoV-2 are not at risk of…
This website uses cookies.